
Nibiru Network Whitepaper 1.2
by the Nibiru Network Trust
NIBIRU NETWORK
A decentralized cloud
Abstract
The internet has drastically changed over the past 30 years, with the largest cloud-based companies and some governments dominating every layer of the internet and profiting from their users' private data while restricting access. To address this issue, pioneers have been working on creating value on decentralized networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which enable open services without a central authority. However, high costs and established mining classes make it challenging for new users to enter the space..
Enter Nibiru Network, a decentralized cloud infrastructure that leverages Software-Defined Networking (SDN)/Software Defined Virtual Network (SDVN) technology to provide a secure, open, high-speed, co-constructed, and shared decentralized IP layer network. This network employs Multi Proof of Stake (MPoS), Proof of Flow (PoF), and Proof of Capacity (PoC) consensus protocols to incentivize network development.
Resource Providers contribute infrastructure resources, such as the IP layer network, storage, computing, and Web3 applications. Consumers access these resources using the NBN token, the primary token of Nibiru Network, which has a maximum supply of 1,000,000,000. Contributors can mine for NBN tokens, while Consumers must burn NBN tokens in order to get digital access to the Nibiru Network ecosystem and to use the services, including networking, storage and compute resources.
This decentralized model enables Users to transact and exchange data in a trustless and secure manner without relying on a central entity. With its layer-1public blockchain and smart contract capabilities, Nibiru Network offers a promising alternative to traditional centralized cloud models, providing users with increased privacy, security, and control over their resources and data.
In conclusion, decentralized cloud architectures offer a disruptive technology that has the potential to revolutionize how we process and exchange data. Nibiru Network is a prime example of a decentralized cloud infrastructure that leverages blockchain technology to provide a secure and scalable platform for Web3 applications.
This paper aims to cover the following topics:
- The difficulties associated with centralized cloud and systems
- How SDN/SDVN technology plays a role in resolving these challenges, with a focus on its implementation in the Nibiru Network Project
- The Nibiru Network and its primary consensus mechanism, including the functions of MPoS, PoF, and PoC.
- The economic model and marketplace for network resources, such as storage, bandwidth, and edge computing nodes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nibiru Network: A Groundbreaking Development in Decentralized Infrastructure
Layer 1 decentralized blockchains have yet to reach their full potential. The "Fat Protocol" thesis, which suggests that Layer 1 protocols will capture the majority of value in the blockchain ecosystem, is invalid for Layer 1s that seek real-world adoption at scale. Layer 1s must provide decentralized IT resources in a cost-competitive manner, making them price takers rather than price setters.
Nibiru Network presents an opportunity to establish a rational resource model for decentralized computing, data transfer, and storage. Layer 1s need rational resource pricing for the utilities they provide, so that enterprises can manage protocol resource costs on a market-standard basis that is compatible with real-world requirements.
Nibiru Network is an evolutionary step in the development of secure, decentralized cloud infrastructures designed to connect the Web2 and Web3 worlds by tokenizing real resources and activities (work). Combining SDN/SDVN technology with blockchain technology, Nibiru Network offers a unique value proposition that encompasses decentralized networking, storage, and compute capabilities. This approach provides a secure, reliable, and transparent data store and transactional environment, while also enabling agility, scalability, performance, and affordability.
To encourage continued development and growth, Nibiru Network leverages three consensus protocols: Multi Proof of Stake (MPoS), Proof of Flow (PoF), and Proof of Capacity (PoC). These protocols facilitate the creation of a comprehensive and seamless economic ecosystem that connects virtual economies on the blockchain with real-world applications off-chain.
Compatibility with other EVM-based software/technologies provides developers with a convenient and intuitive way to migrate or deploy their projects to Nibiru Network. By offering this level of compatibility and flexibility, Nibiru Network has the potential to become a key Layer-1 in the blockchain landscape, empowering developers to create decentralized applications and driving the evolution of the entire blockchain industry.
Overall, Nibiru Network represents a groundbreaking development in secure, decentralized infrastructures that support Web2 and Web3 applications, bridging the present and future.
2 ABBREVIATIONS & DEFINITIONS
Application Developer(s): Application Developers provide Users with various real applications developed based on the Nibiru Network protocol. The services provided are mapped to the PoF or PoC consensus protocols. Application Developers are also referred to as “Contributors”.
Consumer(s): Consumers burn NBN tokens to gain digital access to Nibiru Network ecosystem and, through the protocol, use the Credit Vouchers to access various services in Nibiru Network, such as bandwidth, storage, and application.
Contributors: Contributors participate in Nibiru Network either as Resource Providers and/or Application Developers. Contributors may contribute to block generation and verification, provide IP layer network and/or storage and develop applications in Nibiru Network.
Credit Voucher(s): Credit Vouchers are created through the protocol, when Consumers burn NBN tokens to gain digital access to use services on Nibiru Network . Through the protocol, consumers access services on Nibiru Network, such as bandwidth, storage, and applications, using Credit Vouchers.
Investor(s): Investors provide funds, technology, market, and other resources for various projects on the Nibiru Network blockchain.
MPoS: Multi Proof of Stake: Multi Proof of Stake (MPoS) is a layer-1 consensus algorithm used in Nibiru Network that is based on the original Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, but with modifications to address certain issues or limitations. It presets two pools of candidate nodes with different proportions of candidates (upper and lower house systems). In each round of witness node election, a corresponding number of nodes are selected according to the equity algorithm to give the right to produce blocks (that is, verification node), and at the same time combined with the benefit algorithm to ensure that each participant can get the opportunity to produce a block.
NBN/NBN token(s): NBN is the native token of the Nibiru Network blockchain. As a utility token, it provides a User with access to the Nibiru Network ecosystem and services, and it incentivizes user participation.
PoC: Proof of Capacity: Proof of Capacity (PoC) is a consensus mechanism used in Nibiru Network to validate valid storage capacity.
PoF: Proof of Flow: Proof of Flow (PoF) is a consensus mechanism designed for Nibiru Network to validate the flow of assets and data traffic through the network. PoF is based on combining static bandwidth support and dynamic flow work that maps real services in the real world to network traffic and converts verified valid traffic into rewards on the chain.
Resource Provider(s): Resource Providers are responsible for maintaining system stability at the blockchain layer, IP network service layer, storage service layer, and Web3 application layer. They provide various services in the real-world application market. Resource providers consist of block generation and verification Contributors (using MPoS), IP layer network Contributors (using PoF), storage Contributors (using PoC), and application Contributors (mapped to PoC and PoF). Resource Providers are also referred to as “Contributors” and/or miners.
SDN (Software-Defined Networking): Software Defined Networking (SDN) is a network architecture that allows network administrators to manage network services and traffic flows using a centralized software controller, separate from the underlying physical network infrastructure. SDN achieves this by separating the control plane from the data plane, allowing administrators to program network behavior through software rather than configuring individual network devices. This approach provides greater flexibility and agility in network management, making it easier to respond to changing network requirements and traffic patterns.
SDVN (Software Defined Virtual Network): SDVN is a virtual network architecture that uses software-defined networking principles to create virtual network segments or overlays on top of physical networks such as the Internet and LAN. It adopts advanced technologies, including multi-code packet encryption, multi-layered, network slicing, DLT, and next-hops, to build a "network-data-application" autonomous platform that provides a highly reliable, scalable, and programmable secure distributed network infrastructure for Web2/Web3 applications. SDVN extends various application scenarios, including decentralized networks, identities, data, and computing, while integrating with the encrypted digital economy. Its ultimate goal is to create a permanent next-generation Internet digital economic ecology that is shared by all participants, connecting the digital and physical worlds.
Storage Node: The Storage Node participates in PoC and PoF protocols to store and retrieve data on Nibiru Network and receives PoC & PoF rewards for its participation. The production is constrained by the node’s storage and bandwidth capacity.
Token Holder(s): Token Holder(s) hold NBN tokens.
Traffic Node: The Traffic node participates in the PoF protocol by providing various application services to generate valid value traffic. This node receives PoF rewards for its participation. The production is limited by the node's bandwidth capacity.
User(s): Users are participants, such as Consumers or Contributors, who either use or provide services on Nibiru Network.
Validator Node: The Validator node participates in the MPoS protocol to validate transactions on Nibiru Network. This node receives MPoS rewards for its participation. The production is restricted by the node's rights, penalty points, and verification times.
3 Overview of the Nibiru Network
3.1 Nibiru Network Reduces the Risks Associated with Centralized Cloud
In today's world, data is of paramount importance and can be categorized into commodity and tool properties. The capacity to exchange data, a vital aspect of the commodity property, facilitates data flow. As the driving force behind digital transformation, data is the lifeblood of the digitization process. With tens of billions of smart devices connected to the internet, data interactions have reached unparalleled heights.
However, big tech companies that control centralized cloud storage systems remain unchallenged, wielding enormous power, wealth, and information through monopolization. Their centralized control stifles competition, manipulates markets, influences politics, and restricts data flow. Centralized systems also leave data vulnerable to hacking, breaches, or power surges, potentially causing catastrophic consequences.
Despite a decade of leaks and data loss in cloud computing, centralized network architecture continues to be strained. The Internet of Things (IoT) will challenge communication networks and data centers, as the demand for personalized, instantaneous, and mobile real-time data grows. Massive terminal communication in IoT requires low latency.
Centralized Non-Fungible Token (NFT) marketplaces and metaverses pose significant risks due to central authorities controlling operations, functions, and data. These systems are susceptible to censorship, data leaks, and single points of failure. Conversely, decentralized metaverses empower users, fostering innovation, open-source code, peer-to-peer projects, distributed computing, and smart contracts. Decentralized digital currencies will enable secure, fully decentralized payments within virtual worlds.
The existing centralized Internet model entrusts data control and distribution to gatekeepers. Nibiru Network is an independent Layer-1 blockchain solution with its Software-Defined Networking (SDN)/Software-Defined Virtual Network (SDVN) overlay network, providing a decentralized cloud alternative for Consumers and Resource providers.
While SDN/SDVN has been a prevalent technology in enterprise networking for the past decade, Nibiru Network's integration of blockchain technology sets it apart. Nibiru Network utilizes a public blockchain system to securely store data and ensure seamless network operations.
In addition, the Nibiru Network blockchain introduces cutting-edge consensus mechanisms that encourage network expansion and incentivizes Resource Providers to contribute their infrastructure resources in three distinct ways. By establishing a trustless decentralized value network for data communication, powered by distributed IT infrastructure resources, Nibiru Network paves the way for an information superhighway.
3.2 What is Nibiru Network
Nibiru Network is a decentralized and secure cloud infrastructure that facilitates the development of Web3 applications through the use of three consensus protocols: Multi Proof of Stake (MPoS), Proof of Flow (PoF), and Proof of Capacity (PoC). The platform is built on SDN/SDVN technology, enabling Resource Providers to contribute resources, and Consumers to use the services.
The key feature of Nibiru Network is the provision of a secure, open, high-speed, co-constructed, and shared decentralized IP layer network based on SDN/SDVN networking technology. The network provides an open and closed-loop economic ecosystem where Users can benefit from each other's services. Resource Providers are responsible for maintaining system stability across the blockchain layer, IP network service layer, storage service layer, and Web3 application layer, offering a variety of services in the real-world application market.
Nibiru Network is a Layer-1 public blockchain with robust smart contract capabilities that are fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This compatibility allows developers to migrate or deploy their projects from Ethereum, offering Users the same dApp experience at a lower cost.
Nibiru Network’s native token is NBN, which has a maximum supply of 1,000,000,000. Resource Providers can mine for NBN, while Consumers burn NBN, through the protocol, in order to get digital access to Nibiru Network's ecosystem. This incentivizes the development of the network and ensures the circulation of the NBN token within the ecosystem. NBN tokens are also used to facilitate traffic consensus PoF and effective storage consensus PoC powered by the SDN/SDVN technology.
The mining process in Nibiru Network involves various Contributors, such as block generation and verification Contributors, IP layer network Contributors, storage Contributors, and application Contributors. The consumption of services on the network requires the burning of NBN tokens, through the protocol, which reduces the supply of tokens over time, supporting the NBN and the long-term success of Nibiru Network.
In summary, Nibiru Network is a decentralized and secure platform for Web3 applications that incentivizes development through the use of consensus protocols, and provides a secure IP layer network. The network operates on a collaborative relationship between Consumers and Contributors and offers powerful smart contract capabilities that are fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
3.3 Nibiru Network Benefits
1. Service. Earn
In the Nibiru Network ecosystem, the participation of both Consumers and Contributors is vital for the growth and enrichment of the overall application ecosystem. Consumers burn NBN tokens, through the protocol, to gain digital access to Nibiru Network services such as bandwidth, storage, and applications, while Contributors receive rewards for their contributions to the network.
The partnership between Consumers and Contributors fosters a collaborative and symbiotic relationship, creating a sustainable and prosperous ecosystem that benefits all participants. The combination of consumer demand and contributor input enables the network to maintain stability, enhance its capabilities, and expand its services, ensuring that it remains a valuable resource for its Users.
2. Connecting “On-Chain” and “Off-Chain”
Nibiru Network bridges the gap between the "on-chain" and "off-chain" worlds by utilizing IP layer network traffic consensus PoF and effective storage consensus PoC, powered by SDN/SDVN technology. This technology enables the conversion of the business value of real-world applications into digital tokens on the blockchain, providing a simple, low-cost, and convenient way for more Investors and Consumers to directly participate in the blockchain digital economy.
Through this innovative approach, Nibiru Network expands the possibilities of the digital economy by integrating it with the real-world economy, creating new opportunities for growth, investment, and collaboration. By facilitating this connection between the on-chain and off-chain worlds, Nibiru Network paves the way for a more inclusive and accessible blockchain ecosystem that benefits all participants.
3. Secure and Decentralized
The use of fully distributed encrypted IP layer networks built on SDN/SDVN technology in Nibiru Network provides a flexible, scalable, and high-performance communication environment for all Users, including Contributors and Consumers. This decentralized approach ensures the security and privacy of all Users on the platform.
By utilizing this cutting-edge technology, Nibiru Network offers a secure and efficient communication infrastructure that enables seamless collaboration between Users. This allows for a dynamic and adaptive network that can quickly respond to changes in user demands while maintaining the highest level of security and privacy.
4. Closed-Loop Economy
With its decentralized and secure features, Nibiru Network offers Users a diverse range of services, including both on-chain and off-chain offerings. Resource Providers can earn value in return for their services, creating a closed-loop economy between Resource Providers and Consumers.
This economic model promotes the continued growth and success of the Nibiru ecosystem, as it incentivizes Resource Providers to maintain system stability across the blockchain layer, IP network service layer, storage service layer, and Web3 application layer. By offering various services in the real-world application market, Resource Providers contribute to the enrichment of the overall application ecosystem.
Furthermore, the closed-loop economy ensures that Contributors are rewarded for their resource contributions, creating a sustainable and prosperous ecosystem. This model also benefits Consumers, who can access a wide range of services, while contributing to the success and growth of Nibiru Network.
5. Consume. Burn.
In Nibiru Network, Consumers burn NBN tokens to gain access to the Nibiru Network’s services through the protocol, leading to the gradual burning of NBN tokens and a reduction in supply. This process guarantees the enduring success of both NBN tokens and Nibiru Network by fostering a balanced, sustainable ecosystem that benefits all participants.
As NBN tokens are burned, Consumers not only gain access to the Nibiru Network’s services, but also play an active role in decreasing token supply. This strategy safeguards the NBN token's value and enhances it over time, ensuring the long-term prosperity of both the token and the network.

3.4 Nibiru Network Architecture

3.5 Features of the MPoS Consensus Mechanism
The MPoS (Multi Proof of Stake) consensus mechanism is an improvement based on the traditional PoS protocol. This system is designed to address the scalability and security issues faced in other networks, while also providing faster transaction processing times and lower energy consumption.
A key feature of MPoS is its dual-chamber model, which divides the candidate nodes into two separate pools with different proportions of candidates. The upper and lower house system ensures that nodes with a larger number of pledges have more opportunities to produce blocks, while smaller nodes also have a chance to participate in the block production process, thereby avoiding class solidification and consensus rigidity. In other words, in each round of witness node election, a corresponding number of nodes are selected according to the equity algorithm to give the right to produce blocks (that is, verification node), and at the same time combined with the benefit algorithm to ensure that each participant can get the opportunity to produce a block.
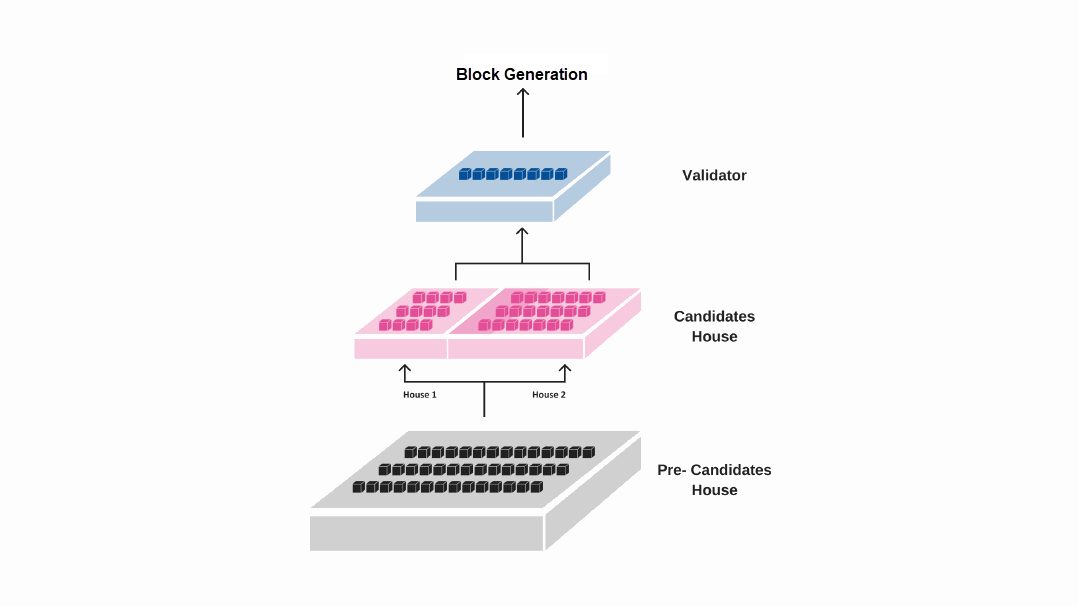
The MPoS consensus mechanism also offers faster block confirmation times. In the MPoS network, a block is solidified immediately upon its production and then confirmed by 21 verifiers within 10 seconds, resulting in faster convergence speeds and reduced rollback risks.
Moreover, the MPoS network has a stable distribution of block generation time, producing a block every 10 seconds with an average waiting time of 6 seconds for transaction processing. This ensures that the network maintains optimal performance and transaction processing speeds.
The MPoS verification process as used by Nibiru Network, is also expanded beyond transaction verification, as the verifier is responsible for verifying participants in the PoC and PoF protocols, with additional responsibilities and benefits compared to traditional PoS. This expanded scope of verification ensures the integrity and security of the network.
Another key advantage of MPoS is its low participation threshold. The 100 NBN pledge entry threshold is far lower than other networks that adopt PoS consensus in the industry. This allows anyone to participate in the network as a verifier, ensuring decentralized participation and a more secure network.
Finally, the MPoS network has a built-in mechanism that allows for faster detection of issues with validator participation in a single slot. This means that potential problems with the network can be identified and addressed quickly, ensuring optimal network performance and security.
Overall, the MPoS consensus mechanism offers a range of features and benefits that make it an industry-recognized optimal solution for blockchain networks. Its fairer dual-chamber system, faster block confirmation times, stable block generation times, expanded verification process, low participation threshold, and faster problem detection makes it a highly secure, efficient, and scalable blockchain solution.
3.6 Protocols of PoF and PoC based on layer-2 ZK-rollup
Nibiru Network utilizes a Layer-2 ZK-rollup solution to provide workload aggregation, Credit Vouchers, and unified reward distribution for nodes that participate in the PoC and PoF consensus protocols.
The ZK-rollup solution is a Layer-2 scaling solution that aggregates multiple transactions into a single transaction, minimizing the amount of data that needs to be processed on the main chain. This aggregation reduces transaction fees and increases the overall efficiency of the network.
By adopting this solution, Nibiru Network is able to streamline its processes, facilitating workload aggregation and Credit Vouchers for nodes participating in the PoC and PoF protocols. Additionally, the unified reward distribution ensures that all nodes are rewarded fairly and transparently, promoting a more equitable ecosystem.

3.7 Technical Specifications of Nibiru Network's Economic Model
3.7.1 Nibiru Token Types and NBN TWAP
The NBN token is the native token of the Nibiru Network blockchain. It is both tradable and transferable. Through the protocol, consumers burn NBN tokens to gain digital access to the Nibiru Network’s services. Through the protocol, the burning of NBN tokens mints Credit Vouchers that are used within the Nibiru Network ecosystem. The Credit Vouchers are mapped to valid storage and IP network traffic. They cannot be traded and can solely be used within and to access the Nibiru Network’s resources and services.
The value of one Credit Voucher remains constant within the Nibiru Network ecosystem and can only be minted through the burning of NBN tokens, through the protocol. The conversion ratio of Credit Voucher to NBN is determined based on the TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price). Oracle machines provide the price of NBN at regular intervals, and when enough new data is gathered, the blockchain calculates a new NBN/$ USD or official currency price. This price remains valid until new valid data is submitted, prompting a new price correction.
The NBN TWAP update interval is every 60 blocks or about 10 minutes. If the number of oracle machines providing the quotation reaches (n/2)+1 within 24 hours, the blockchain uses the remaining prices to calculate the average value, removing the highest and lowest values. This average value is then used as the TWAP for the next credit exchange for NBN until a new price update occurs.
For a price submission to be valid, it must have been submitted within the last 25 hours but must be older than 1 hour. This allows the blockchain to calculate a trailing 24-hour median while also providing a buffer against outlier price inputs in the most recent 60 minutes.
3.7.2 Nibiru Network Reward Distribution
The following section provides a brief summary of network rewards of the protocol, which follow a time-based logistics (sigmoid population) curve, where allocations are currently split between MPoS, PoV, PoC and PoF based on fixed percentage allocation. The intention is to shift to a dynamic allocation model once network usage patterns have been analyzed at greater scale.
Formula:
We employ a calibrated sigmoid population curve, P(t):

Where t is the Calculation Period counter (t ∈ [0,∞)), k and c are constants to be resolved from the initial supply P(0), and a half-life inflection point of the curve, expressed in Calculation Periods t0.5.
The curve has an initial supply of 1% and a half life of 60 months.

3.7.3 Valid Traffic
Traffic refers to the movement of data within the Nibiru Network ecosystem. “Valid Traffic” is the upstream network traffic generated by Consumers using Nibiru Network. Through the PoF protocol, NBN tokens are minted when network Contributors provide Valid Traffic to Consumers. Those network Contributors are rewarded by the NBN tokens minted through the PoF protocol.

3.7.4 Valid Storage
Storage refers to storage provided by storage Contributors on Nibiru Network for Consumers. “Valid Storage” means that the storage on Nibiru Network used by Consumers is available, reliable and verifiable.
When Consumers gain access to Nibiru Network, through the protocol, their NBN tokens are minted into Credit Vouchers that are used to access resources provided by storage Contributors. Through the PoC protocol, NBN tokens are minted when storage Contributors provide Valid Storage to Consumers. Those storage Contributors are rewarded by the NBN tokens minted through the PoC protocol.

3.7.5 Mining Methods

3.7.6 Consumer Access to Nibiru Network Services and The Minting Process

Application and services use case illustration:
- Consumers buy NBN tokens on exchanges.
- Consumers burn NBN tokens into Credit Vouchers, through the protocol, to be used to access the services on the Nibiru Network ecosystem.
- Consumers access the services hosted on Nibiru Network, such as video, bandwidth, storage, applications etc., using the credit from the Credit Vouchers, through the protocol.
- These services generate Valid Storage or Valid Traffic.
- Valid Storage will reward NBN tokens to storage Contributors through the PoC protocol; other dApp applications will generate Valid Traffic and reward NBN tokens to network Contributors through the PoF Protocol.
3.7.7 Nibiru Network Use Case: Video Bloggers (Real Application Contributors)
- Video bloggers or Vloggers (Contributors) have the capability to create their own private network on Nibiru Network and deploy video applications on the mining machines within the network. They have the ability to determine their own traffic credit value, provided they do not exceed the network benchmark price limits.
- Consumers burn their NBN tokens into Credit Vouchers, through the protocol, to join the vloggers' private network.
- Consumers watch the video files in the blogger’s mining machine online and use the corresponding Credit Vouchers for the network data traffic generated by the video stream (complete the process of mapping specific applications to Valid Traffic).
- The Valid Traffic generated mints NBN tokens that are distributed and rewarded to video bloggers (Contributors) through the PoF protocol.
Issue NBN rewards based on Valid Traffic (credit corresponding to traffic)

3.7.8 Nibiru Network Supported Application Range
Nibiru Network supports a wide range of applications using Web3 technology, which combines blockchain, distributed network, distributed storage, and distributed computing.
Nibiru Network utilizes an IP layer network to ensure private networking and encrypted communication. Users can create, own, share, store, execute, and trade data in a decentralized manner, while also leveraging edge computing, edge-cloud collaborative computing, and distributed computing for efficient calculation.
To facilitate transactions and consumer services, through the protocol, NBN tokens are burnt into Credit Vouchers, according to the market price. The resulting Credit Vouchers can be used to get digital access to various products and services available on Nibiru Network, through the protocol.
3.8 Account Types and Staking/Locking Rule in Blockchain Networks
3.8.1 MPoS, PoF, PoC Node and General Account Structure Types

Delegated Address Rules:
One delegation address can only be pledged to one MPoS node. If you want to pledge other MPoS nodes, you need to use a new delegation address.
3.8.2 Staking and Locking
In terms of staking and locking periods, Nibiru Network employs specific lock-up and lock-release rules for pledges on Multi Proof of Stake (MPoS), Proof of Flow (PoF), and Proof of Capacity (PoC) protocols. Pledges on these protocols are subject to a one-year lock-up period. Upon completion of the lock-up period, rewards and released pledges are subject to a 30-day lock-up period, followed by a 365-antenna linear release. Under this model, the locked amount is gradually released over a 365-day period, with a proportionate amount being released each day.
For delegators, the stake freeze period is seven days. This means that after delegating tokens, a delegator cannot withdraw them for a period of seven days. These lock-up and freeze periods help to ensure stability and security within the Nibiru Network ecosystem, promoting the long-term growth and success of the platform.
4 Legal Disclaimer, Representations, and Warranties
4.1 Disclaimer
This Whitepaper aims to provide an explanation of Nibiru Network, a next-generation decentralized secure network operated by the Nibiru Network Trust, a trust incorporated under the laws of England and Ireland, represented, by Granit Trust Services SA, a Swiss company registered under the number CHE-425.412.970 and having its registered address at Rue du Grand-Chêne 8, 1003 Lausanne, acting as the trustee of the Nibiru Network Trust.
The native token associated with Nibiru Network is NBN. This token can be mined by Contributors and can be used by Consumers to access services within the Nibiru Network's ecosystem by using Credit Vouchers. It is important to note that the NBN tokens are not intended to be considered securities in any jurisdiction. Rather, they are utility tokens by nature.
This Whitepaper does not intend to constitute an offer of buying securities or a solicitation for investment in securities in any jurisdiction. Additionally, it does not provide any recommendations or advice to sell or purchase NBN tokens. This document cannot be the basis for making any investment decision or concluding an investment agreement. The NBN tokens are intended solely for the purposes as contained within this Whitepaper.
As a potential Investor, it is important to note that if you are a citizen or resident of any jurisdiction where cryptocurrencies are banned or restricted either partially or completely, you shall not purchase any NBN tokens. It is important to comply with the regulations and laws of your jurisdiction in relation to cryptocurrency investments. Moreover, the information provided in this Whitepaper has not been approved or checked by regulatory bodies and authorities. Publishing and distributing this Whitepaper does not imply compliance with the laws, regulatory requirements, rules or regulations. Therefore, there may be some ambiguities and risks associated with Nibiru Network and its operations, as well as the use of NBN tokens.
Since the Whitepaper is provided for informational purposes only and cannot be used as a legal document or investment agreement. It is strongly recommended to read the following sections before making any investment decisions.
4.2 No Representations and Warranties
We hereby disclaim and waive any representation, warranty or undertaking, express or implied, in any form whatsoever to any entity or person, as well as any representation, warranty or undertaking with the accuracy or completeness of any information provided in this Whitepaper. This Whitepaper is for informational purposes only and should not be relied upon for making any investment decisions. We do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, reliability or timeliness of any information contained herein, nor do we make any representation or warranty regarding the suitability or fitness for any particular purpose of any information, product, service, or platform described in this Whitepaper. Any reliance on this Whitepaper is at your own risk. We assume no responsibility for any errors or omissions in this Whitepaper or for any loss or damage arising from or in connection with the use of this Whitepaper or any information contained herein.
4.3 Representations and Warranties Provided by You
By receiving and/or accessing any information provided in this Whitepaper or any part thereof, you represent and warrant to Nibiru Network the following:
- You agree and acknowledge that the NBN tokens are intended solely for use as utility tokens within the Nibiru Network ecosystem and do not constitute any kind of currency, debt security, stock or share, right, option, or derivative in relation to any debt obligation, share, or stock, unit in a scheme of collective investment, unit in a business trust, derivative unit in business, or any other security or class of securities, under the laws of any jurisdiction.
- You confirm that you have a basic understanding of the operation, functionality, use, storage, transfer mechanisms, and other material features of cryptocurrencies, software systems based on blockchain, wallets for cryptocurrencies or other related tokens storage mechanisms, and the technology of blockchain and technology of smart contracts.
- You acknowledge and agree that our businesses as well as systems and their operations may contain several risks and uncertainties, including but not limited to, risks associated with the development and implementation of Nibiru Network, regulatory and legal risks, risks associated with the use and exchange of cryptocurrencies and other related tokens, and market and price volatility risks.
- You acknowledge and agree that to the maximum extent possible by the applicable laws, rules and regulations, we shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, special, punitive, or consequential damages, including but not limited to, loss of income, profits, or loss of use or data, caused by or arising from any reliance on any part of this Whitepaper by you or any other person.
- You agree and acknowledge that the contents of this Whitepaper do not constitute any offer, solicitation or sale of any securities, investment products or financial instruments in any jurisdiction, and that the purchase and/or sale of NBN tokens shall be subject to applicable laws and regulations in your jurisdiction.
- You agree and acknowledge that Nibiru Network is not responsible for any unauthorized use or access to your personal data or other confidential information resulting from any breach of security or other cyber-attacks or incidents that may occur in connection with the use of Nibiru Network or the NBN tokens.
- You confirm that you are not a citizen or resident of any jurisdiction where the purchase, ownership, or use of cryptocurrencies or related tokens is prohibited, restricted, or otherwise illegal.
- You agree and acknowledge that Nibiru Network may modify or amend this Whitepaper at any time without notice and that any such modification or amendment shall be binding on you upon publication on the Nibiru Network's website.
4.4 Cautionary Note on Forward-Looking Statements
We would like to caution readers that certain statements and claims made in this Whitepaper may be considered forward-looking statements, which involve risks and uncertainties that may result in materially different outcomes than those projected or anticipated. Forward-looking statements may contain words such as "believe," "if," "will," "anticipate," "plan," "would," "possible," "aim," "target," "could," "estimate," "expect," "intend," "may," "should," or other similar terms, but are not limited to these terms alone. Forward-looking statements in this Whitepaper include, but are not limited to, information about the financial position, plans, prospects, and business strategy of Nibiru Network and the future of cryptocurrencies and the banking industry. These statements are projections, not accomplished facts. They include statements regarding the Nibiru Network's profitability, prospects, and revenue, as well as possible industry trends.
We would like to emphasize that forward-looking statements are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that may cause actual results, performance, or achievements to differ materially from any future results, performance, or achievements that were initially expected or intended by such forward-looking statements. Such factors include:
- changes in the cryptocurrency market, political or social conditions, or the regulatory environment in countries where we conduct our operations and businesses;
- risks and uncertainties related to our ability to implement our future plans and business strategy, as described in this Whitepaper;
- changes in the interest/exchange rates of crypto and fiat currencies;
- shifts in expected growth strategies and anticipated internal growth;
- changes in the availability of NBN tokens and the amount paid to us in connection with our respective businesses and operations;
- alterations in the remuneration of our employees, whom we primarily rely on to operate and manage related business operations and activities;
- changes in the preferences of our customers;
- alterations in the market competitive environment that may affect our ability to realize our plans and compete;
- changes in the future capital requirements for us and the availability of sufficient funding and resources to finance such needs;
- unsafe conditions that may threaten public and social safety, such as war, revolution, or terrorism;
- emergency and natural disasters that may affect the ability of our team to implement the working plan mentioned in this Whitepaper; and
- other factors outside of our control.
We would like to stress that all forward-looking statements made or expressed by us or our representatives are entirely qualified in full by the above-mentioned factors. Taking into consideration that these risks and uncertainties could influence the actual future results, could differ materially from the reality, or the expected attainments of Nibiru Network, and could be materially different from initially expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements in this Whitepaper, unjustified trust must not be put in these statements. We caution readers that they should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. These statements are relevant only as of the date of this Whitepaper.
Neither we nor our representatives take any responsibility or give any guarantee that future results will correspond with the aforementioned forward-looking statements. The practical results, progress, and achievements of Nibiru Network may be materially different from those stated in these forward-looking statements.
No information contained in this Whitepaper should be perceived as a promise, representation of commitment, or undertaking as to the future performance of our policies. In addition, we, hereby, waive any responsibility for updating any of those aforesaid forward-looking statements, or publicly announced revisions to these forward-looking statements reflecting future progress, events, or circumstances, even if new information becomes publicly available or other unexpected events take place in the future.
4.5 Risk Warning
By participating in the NBN tokens and Nibiru Network, you acknowledge and accept the risks associated with them. We want to emphasize that Consumers who engage in this project understand and are willing to bear the corresponding risks and consequences personally.
We cannot be held liable for any direct or indirect losses that you may incur due to participating in NBN tokens or Nibiru Network. These losses may include investment risks arising from consumers' participation in the projects recommended by Nibiru Network, errors or inaccurate information resulting from personal understanding, and losses arising from individual trading in all types of blockchain assets.
We cannot guarantee that the value of NBN tokens will appreciate, and there is a possibility of a decline in its value. Individuals who do not use Nibiru Network correctly may lose their right to use the corresponding tokens. Please note that acquiring, possessing, transacting with, or dealing with NBN tokens does not grant any individual the right to participate, control, or make decisions on Nibiru Network. We are not a bank or investment in the conventional sense and, therefore, do not fall under banking regulations.
The regulatory attitude of governments towards blockchain and encrypted digital currency industries is still unclear, and the risk of establishing a blockchain industry fund is objective. The blockchain industry is at a very early stage of development, and there are many uncertain risks. In addition, digital currency is stored especially, and fund risks may be caused by human errors. To mitigate fund risks, all large-value digital currencies are stored in multiple wallets + cold storage in joint administration by members of the foundation. This multi-signature method effectively reduces the risk of theft and embezzlement of funds, but these risks still exist and may lead to the final failure of the project.
4.6 Market and Industry Information and No Consent of Other Persons
Please note that this Whitepaper contains market and industry information, and forecasts obtained from market research, publicly available information, as well as internal surveys, reports, and studies. Although such information has been obtained from sources deemed to be reliable, we cannot guarantee the reliability or completeness of such information.
No person, except for our team members, has agreed or consented to include his/her name, personal data, or any information related to this person in connection with this Whitepaper. No one has the right to require such persons to confirm or update the provided information. There is no warranty or assurance that such information may be reliable, accurate, or updated.
We have taken reasonable steps to ensure that the information in this Whitepaper is released accurately and in the proper context. However, we did not conduct any independent review of information extracted from external sources of third parties and did not confirm the accuracy or completeness of such information or the assumptions based on them. Therefore, neither we nor our relevant team members, who are acting on our behalf, shall be obligated to provide any updates on the representations or guarantees regarding the accuracy or completeness of such information.
4.7 Terms Used in the Whitepaper
To facilitate a better understanding of the NBN tokens and the Nibiru Network, certain technical terms and abbreviations have been used in this Whitepaper. Please note that such descriptions and allocated meanings should not be interpreted as being definitive of their entire meanings and may not match industry standard meanings or use. Words suggesting the singular shall, where fitting, include the plural and vice versa. Words importing the masculine gender shall, where appropriate, include the feminine and neuter genders and vice versa. References to persons shall include corporations.
***
Many thanks to those who have helped make this whitepaper possible:
- PlanetX Labs team: technology development and content contributor
- 01X team: tokenomics strategy and re-design
- Florian Ducommun: content contributor and legal advisor
- Luna PR team: branding, content editing and formatting

© 2023 Nibiru Network Trust
Developers
